Atlas sive Cosmographicae by Gerardus Mercator (1595)
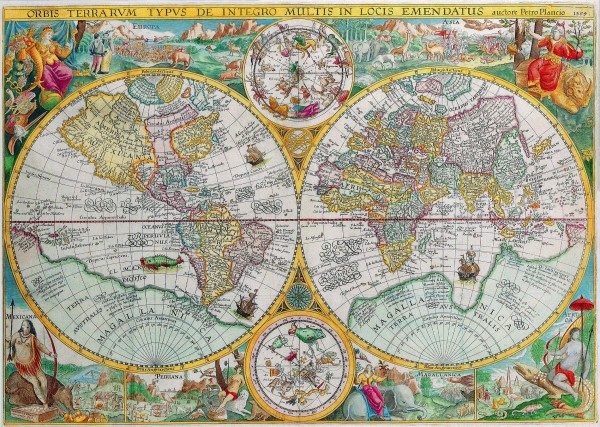
The Fleming Gerard Mercator (1512-1594) is rightfully regarded as the most important scientific cartographer of the Renaissance. With two contemporaries, the geographer Abraham Ortelius and the printer and publisher Christoffel Plantijn,he is considered the father of commercial cartography in the Netherlands.Even during his lifetime his maps, globes and atlases found their way all over the world.Mercator established his reputation mainly through his new projection method. The meridians and parallels are positioned at right angles to each other.If the distances between the meridians are equal, they progressively become larger between the parallels from the equator to the poles.This is why the latitude becomes wider the closer you get to one of the poles and why the part of the Earth in the upper latitudes exhibits excessive proportions.The advantage of this method was the far greater degree of certainty and accuracy in determining shipping routes.In 1585, Mercator published the first three parts of his own book of maps in one volume,which he called Atlas.The second edition appeared in 1589, with the addition of a fourth part. The first complete edition was compiled by his heirs in 1595 one year after his death.Walter Ghim,mayor of Duisburg the city where Mercator had lived for a long time,wrote the accompanying Mercator biography.It was the first time that a book of maps was referred to as an Atlas.Commercially speaking,however,the Atlas was not a success thanks to formidable competition from the Theatrum orbis terrarum by Abraham Ortelius,published in 1570,which by the end of the century had been reprinted more than twenty times.
The Art Of Maps:
The Art of Maps: Map of America from Atlas sive Cosmographicae by Gerardus Mercator (1595)
The Art of Maps: Europa Delineata juxta Obfervationes Excellorum – Vindel 1760
The Art of Maps: PIRI REIS MAP
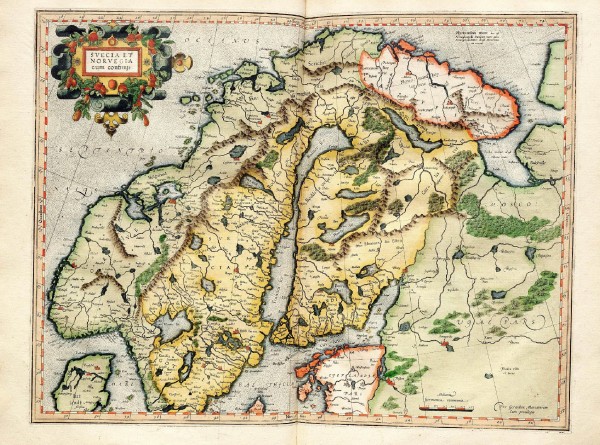
The Art of Maps: Map of Europe from Atlas sive Cosmographicae by Gerardus Mercator (1595)
The Art of maps: John Speed: Asia with the Islands adioyning described, the atire of the people, & Townes of importance, all of them newly augmented . . . 1626
The Art of Maps:Johann Baptiste Homann [California as an Island]
The Art of maps:Matthias Quad – Map of North America 1593
The Art of Maps: Americae Nova Tabula
Sightseeing Map Locations Bulgaria
The Art of Maps: CORNELIS DANCKERTS Nieuw Aerdsch Pley MAP