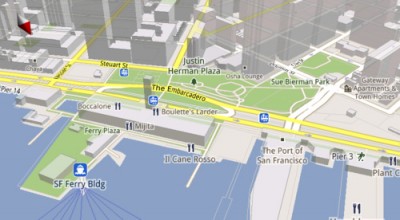
Google has just unveiled their new, refreshed Maps 5.0 app for Android, launching soon. What’s new about it? Well, it renders buildings in 3D, loads faster, works offline and will automatically rotate the map according to the phone’s compass.
Thanks to the small file size and scalability of the new dynamically drawn vector graphics in Maps, the app now renders in realtime, and maps download about 100 times less data—which leads to faster load times and super smooth zooming. (Previously, maps were downloaded as a bunch of tiles and zooming was more of a “snap to” experience.) The new 3D building models will start to appear as you get down to the street view level, and you can even tilt the map using a two-finger swipe gesture, altering the map’s vertical orientation to offer a sense of a building’s height. Imagine popping out of the subway in NYC and instantly recognizing where you’re at by checking out the buildings around you in 3D. 100 cities, like New York, will be supported from the outset.
But perhaps the coolest part of the updated app are the rotation tools. You can rotate the map using the multitouch screen, or let the app rotate itself in accordance with the compass. So if you’re walking through a busy city, the map will turn as you turn, hopefully preventing the user from losing their sense of direction. And if you want a different look at the map, you can move two fingers in a circular motion to rotate the map to your liking.
Also included in the update is an offline mode that will remember areas you’ve visit the most, and cache those maps in the background so that if one’s connection should drop out, they won’t be without navigation. Maps downloads and caches data from your most frequently visited areas overnight when you’re connected to Wi-Fi. A quick demo we saw impressed us with how the vast majority of New York City stayed in memory—even 3D building models and zooming down 2-3 layers in the map—after the phone was switched to offline mode. Google says that this should compensate for 90 percent of the times the app currently fails when the connection is bad—in Navigation it’ll even re-route you if you miss a turn in an area where the signal drops.
The minimum requirements for the new Maps will let it run on any phone running Android 1.6 Donut, but features such as the dynamic rendering and map rotation will only work on more advanced hardware—basically, it’s gotta be as powerful as the original Motorola Droid, though YMMV. It’s a pretty incredible experience, and we can only hope it shows up on other non-Android phones with Google Maps sooner instead of later.


