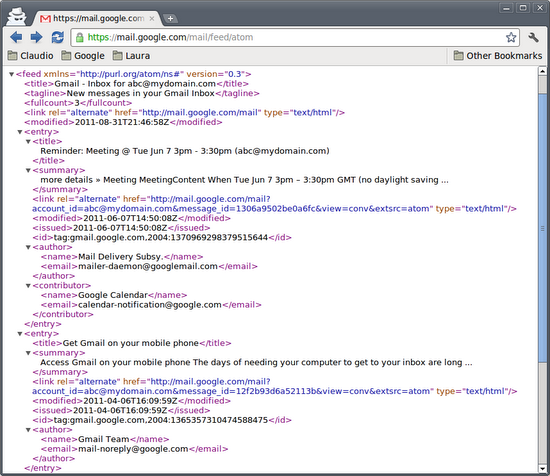
Gmail servers support the standard IMAP and POP protocols for email retrieval but sometimes you only need to know whether there are any new messages in your inbox. Using any of the two protocols mentioned above may seem like an overkill in this scenario and that’s why Gmail also exposes a read only feed called Gmail Inbox Feed which you can subscribe to and get the list of unread messages in your inbox.
The Gmail Inbox Feed is easily accessible by pointing your browser to https://mail.google.com/mail/feed/atom and authenticating with your username and password if you are not already logged in.
Using basic authentication to access the inbox feed doesn’t provide a very good user experience if we want delegated access. In that case, we should instead rely on the OAuth authorization standard, which is fully supported by the Gmail Inbox Feed.
OAuth supports two different flows. With 3-legged OAuth, an user can give access to a resource he owns to a third-party application without sharing his credentials. The 2-legged flow, instead, resembles a client-server scenario where the application is granted domain-wide access to a resource.
Let’s write a .NET application that uses 2-legged OAuth to access the Gmail Inbox Feed for a user in the domain and list unread emails. This authorization mechanism also suits Google Apps Marketplace developers who want to add inbox notifications to their applications.
There is no dedicated client library for this task and the Inbox Feed is not based on the Google Data API protocol but we’ll still use the .NET library for Google Data APIs for its OAuth implementation.
Step-by-Step
First, create a new C# project and add a reference to the Google.GData.Client.dll released with the client library. Then add the following using directives to your code:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Mail;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using Google.GData.Client;
The next step is to use 2-legged OAuth to send an authorized GET request to the feed URL. In order to do this, we need our domain’s consumer key and secret and the username of the user account we want to access the inbox feed for.
string CONSUMER_KEY = "mydomain.com";
string CONSUMER_SECRET = "my_consumer_secret";
string TARGET_USER = "test_user";
OAuth2LeggedAuthenticator auth = new OAuth2LeggedAuthenticator("GmailFeedReader", CONSUMER_KEY, CONSUMER_SECRET
, TARGET_USER, CONSUMER_KEY);
HttpWebRequest request = auth.CreateHttpWebRequest("GET", new Uri("https://mail.google.com/mail/feed/atom/"));
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
The response is going to be a standard Atom 0.3 feed, i.e. an xml document that we can load into an XDocument using the standard XmlReader class:
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create(response.GetResponseStream());
XDocument xdoc = XDocument.Load(reader);
XNamespace xmlns = "http://purl.org/atom/ns#";
All the parsing can be done with a single LINQ to XML instruction, which iterates the entries and instantiates a new MailMessage object for each email, setting its Subject, Body and From properties with the corresponding values in the feed:
var messages = from entry in xdoc.Descendants(xmlns + "entry")
from author in entry.Descendants(xmlns + "author")
select new MailMessage() {
Subject = entry.Element(xmlns + "title").Value,
Body = entry.Element(xmlns + "summary").Value,
From = new MailAddress(
author.Element(xmlns + "email").Value,
author.Element(xmlns + "name").Value)
};
At this point, messages will contain a collection of MailMessage instances that we can process or simply dump to the console as in the following snippet:
Console.WriteLine("Number of messages: " + messages.Count());
foreach (MailMessage entry in messages) {
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Subject: " + entry.Subject);
Console.WriteLine("Summary: " + entry.Body);
Console.WriteLine("Author: " + entry.From);
}
If you have any questions about how to use the Google Data APIs .NET Client Library to access the Gmail Inbox Feed, please post them in the client library discussion group.